Operational structure of GPLAB (see user's manual for details):
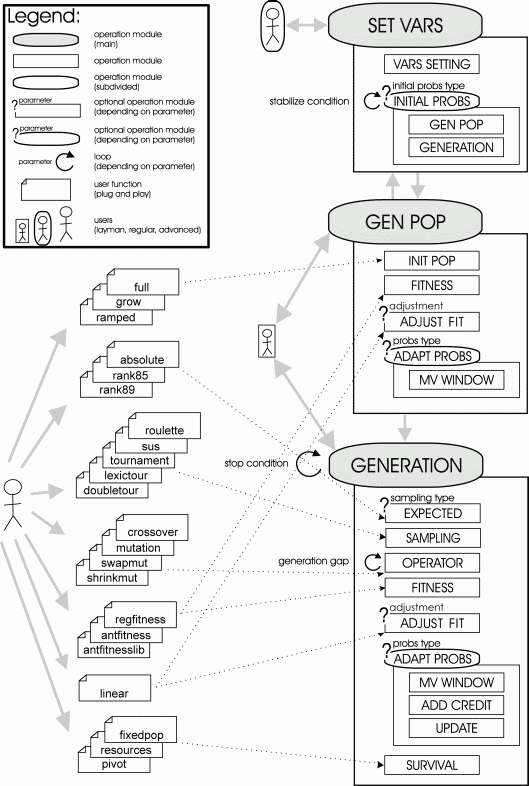
GPLAB is a Genetic Programming toolbox for MATLAB. Most of its functions are used as "plug and play" devices, making it a versatile and easily extendable tool, as long as you have minimum knowledge of the MATLAB programming environment. Here is an illustration of how it works. For details, please read the user's manual. Note: the operational structure is now somewhat outdated, but it may still be useful anyway. The features and references are being updated (2015).
Features of GPLAB
References for some of the features
Illustration of the operational structure
Some of the features of GPLAB (good or bad):
GPLAB does not implement:
Top
References for some of the features
Illustration of the operational structure
References:
[1] Silva S, Almeida J (2003). Dynamic Maximum Tree Depth - A Simple Technique for Avoiding Bloat in Tree-Based GP. In Cantú-Paz E, et al. (eds), Proceedings of GECCO-2003, 1776--1787.
[2] Silva S, Costa E (2004). Dynamic Limits for Bloat Control - Variations on Size and Depth. In Deb K, et al. (eds), Proceedings of GECCO-2004, 666--677.
[3] Silva S, Silva PJN, Costa E (2005). Resource-Limited Genetic Programming: Replacing Tree Depth Limits. In Ribeiro B, et al. (eds), Proceedings of ICANNGA-2005, 243--246.
[4] Silva S, Costa E (2005). Resource-Limited Genetic Programming: The Dynamic Approach. In Beyer H-G, et al. (eds), Proceedings of GECCO-2005, 1673--1680.
[5] Tomassini M, Vanneschi L, Cuendet J, Fernandez F (2004). A New Technique for Dynamic Size Populations In Genetic Programming. In Proceedings of CEC-2004, 486--493.
[6] Cuendet J (2004). Populations dynamiques en programmation génétique. Université de Lausanne, Université de Genève.
[7] Rochat D (2004). Programmation Génétique Parallèle: Opérateurs Génétiques Variés et Populations Dynamiques. Université de Lausanne, Université de Genève.
[8] Rochat D, Tomassini M, Vanneschi L (2005). Dynamic Size Populations in Distributed Genetic Pogramming. In Keijzer M, et al. (eds), Proceedings of EuroGP-2005, 50--61.
[9] Luke S, Panait L (2002). Lexicographic Parsimony Pressure. In Langdon WB, Cantú-Paz E, Mathias K, et al. (eds), Proceedings of GECCO-2002, 829--836.
[10] Luke S, Panait L (2006). A comparison of bloat control methods for genetic programming. Evolutionary Computation 14(3): 309--344.
[11] Davis L (1989). Adapting operator probabilities in genetic algorithms.
In Schaffer JD (ed.), Proceedings of the Third International Conference
on Genetic Algorithms, 61--69.
Top
Features of GPLAB
Illustration of the operational structure
Operational structure of GPLAB (see user's manual for details):

Top
Features of GPLAB
References for some of the features